Overview#
In production or homelab clusters, data loss can occur due to failed upgrades, node corruption, or misconfiguration. A robust backup strategy ensures full cluster recovery with minimal downtime.
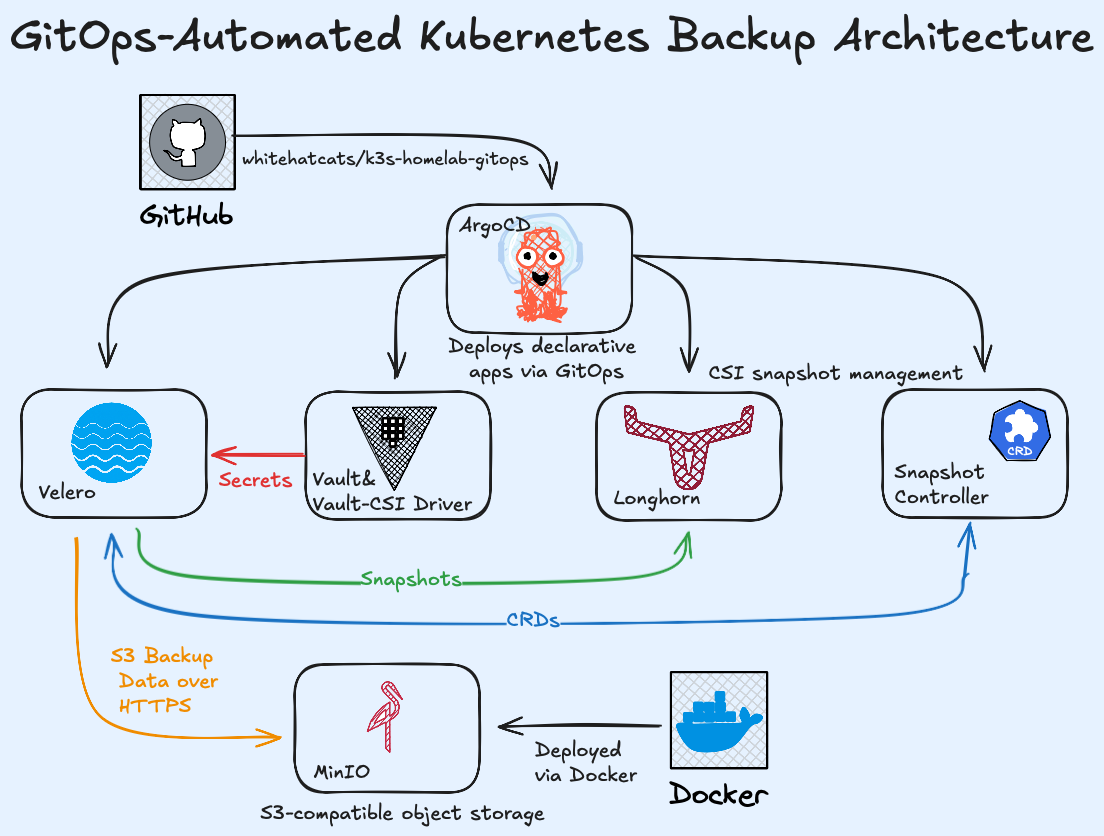
This documentation presents a GitOps-managed backup and disaster recovery architecture for Kubernetes. The configuration integrates Velero for orchestration, Vault CSI for secure secret delivery, Longhorn
for CSI snapshot capabilities, and MinIO as the S3-compatible object storage backend.
The deployment is entirely declarative and automated through Argo CD, ensuring repeatability and reliability.
Each directory represents an Argo CD Application within the GitOps repository, enabling versioned, declarative infrastructure management.
All manifests and configurations are stored and versioned in whitehatcats/k3s-homelab-gitops.
Objectives#
- Automate scheduled cluster and persistent volume backups
- Maintain version-controlled infrastructure definitions
- Secure secrets using Vault and the CSI driver
- Provide visibility through Velero UI
- Support full restoration via Longhorn and Velero snapshots
Architecture#
This backup architecture is built on the following open-source technologies:
- Argo CD — GitOps automation
- Velero — backup & restore orchestration
- Vault CSI Driver — secure secret injection
- Longhorn — persistent volume snapshots
- MinIO — S3-compatible object storage
Below is the folder structure for the YAML manifests presented in this article.
infra/
├── snapshot-controller/
│ ├── app.yaml
│ └── values.yaml
├── velero/
│ ├── app.yaml
│ ├── kustomization.yaml
│ ├── values.yaml
│ ├── velero-s3-spc.yaml
│ └── coredns-pihole-cm.yaml
└── velero-ui/
├── app.yaml
├── kustomization.yaml
├── values.yaml
├── velero-ui-spc.yaml
├── velero-ui-auth-spc.yaml
└── velero-ui-secret.yaml
Step-by-Step Implementation#
1. Snapshot Controller#
Responsible for installing and managing Kubernetes VolumeSnapshot CRDs and controllers required by CSI
drivers such as Longhorn. This ensures compatibility with Velero’s CSI backup features.
Argo CD Application#
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Application
metadata:
name: snapshot-controller
namespace: argocd
finalizers:
- resources-finalizer.argocd.argoproj.io
annotations:
argocd.argoproj.io/sync-wave: "-2"
spec:
project: homelab
destination:
server: https://kubernetes.default.svc
namespace: kube-system
sources:
- repoURL: https://piraeus.io/helm-charts/
chart: snapshot-controller
targetRevision: 4.1.1
helm:
valueFiles:
- $values/infra/snapshot-controller/values.yaml
- repoURL: git@github.com:whitehatcats/k3s-homelab-gitops.git
targetRevision: HEAD
ref: values
syncPolicy:
automated:
prune: true
selfHeal: true
syncOptions:
- CreateNamespace=false
- ServerSideApply=true
- ApplyOutOfSyncOnly=true
Helm Values#
controller:
enabled: true
replicaCount: 1
args:
leaderElection: true
leaderElectionNamespace: "kube-system"
httpEndpoint: ":8080"
image:
repository: registry.k8s.io/sig-storage/snapshot-controller
pullPolicy: IfNotPresent
tag: ""
rbac:
create: true
serviceAccount:
create: true
name: snapshot-controller
volumeSnapshotClasses:
- name: longhorn-snapshot-vsc
annotations:
snapshot.storage.kubernetes.io/is-default-class: "true"
labels:
velero.io/csi-volumesnapshot-class: "true"
driver: driver.longhorn.io
deletionPolicy: Delete
volumeGroupSnapshotClasses: []
leaderElection:
enabled: true
namespace: kube-system
installCRDs: true
2. Velero Backup System#
Velero provides cluster-level backup and restore capabilities, integrating with Longhorn CSI snapshots for persistent volume protection. It connects to MinIO over HTTPS, uses Vault CSI for credentials, and runs daily automated backups for all namespaces.
Argo CD Application#
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Application
metadata:
name: velero
namespace: argocd
finalizers:
- resources-finalizer.argocd.argoproj.io
spec:
project: homelab
destination:
server: https://kubernetes.default.svc
namespace: velero
sources:
- repoURL: git@github.com:whitehatcats/k3s-homelab-gitops.git
targetRevision: main
ref: values
- repoURL: https://vmware-tanzu.github.io/helm-charts
chart: velero
targetRevision: 11.1.0
helm:
valueFiles:
- $values/infra/velero/values.yaml
- repoURL: git@github.com:whitehatcats/k3s-homelab-gitops.git
targetRevision: main
path: infra/velero
syncPolicy:
automated:
prune: true
selfHeal: true
syncOptions:
- CreateNamespace=true
- PruneLast=true
- Validate=false
- ServerSideApply=true
- RespectIgnoreDifferences=true
ignoreDifferences:
- group: apiextensions.k8s.io
kind: CustomResourceDefinition
- group: admissionregistration.k8s.io
kind: MutatingWebhookConfiguration
- group: admissionregistration.k8s.io
kind: ValidatingWebhookConfiguration
Helm Values#
Defines the S3 endpoint, Vault-synced secret, and backup schedule. It also enables the CSI snapshot feature for Longhorn volumes.
image:
tag: v1.17.0
rbac:
clusterAdministrator: true
serviceAccount:
server:
name: velero
metrics:
serviceMonitor:
enabled: true
additionalLabels:
release: kube-prometheus-stack
configuration:
features: EnableCSI
backupStorageLocation:
- name: default
provider: aws
bucket: velero
default: true
accessMode: ReadWrite
credential:
name: velero-s3-secret
key: cloud
config:
region: us-east-1
s3ForcePathStyle: true
s3Url: https://minio-api.techcats.org
publicUrl: https://minio-api.techcats.org
insecureSkipTLSVerify: false
volumeSnapshotLocation:
- name: default
provider: csi
default: true
config:
region: us-east-1
uploaderType: kopia
defaultRepoMaintainFrequency: 24h
repositoryMaintenanceJob:
global:
keepLatestMaintenanceJobs: 3
credentials:
existingSecret: velero-s3-secret
extraVolumes:
- name: secrets-store
csi:
driver: secrets-store.csi.k8s.io
readOnly: true
volumeAttributes:
secretProviderClass: velero-s3-spc
extraVolumeMounts:
- name: secrets-store
mountPath: /mnt/secrets-store
readOnly: true
schedules:
daily-cluster-backup:
schedule: "0 3 * * *"
template:
ttl: "168h"
includedNamespaces:
- '*'
initContainers:
- name: velero-plugin-for-aws
image: velero/velero-plugin-for-aws:v1.13.0
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /target
name: plugins
TLS verification is enforced insecureSkipTLSVerify: false, ensuring Velero only connects to the
MinIO endpoint using a trusted certificate issued by Let’s Encrypt through Traefik’s cert-resolver.
Secret Management via Vault CSI#
The Vault CSI driver mounts secrets from Vault directly into the Velero pod’s filesystem, which also triggers
the automatic creation of a Kubernetes Secret velero-s3-secret.
While the mounted files provide the initial data, Velero itself does not read credentials directly from them.
Instead, it authenticates using the synchronized Kubernetes Secret referenced by the Helm chart’s e
xistingSecret field, maintaining full compatibility with Velero’s native credential workflow while ensuring that no credentials are ever stored in Git or plaintext manifests.
apiVersion: secrets-store.csi.x-k8s.io/v1
kind: SecretProviderClass
metadata:
name: velero-s3-spc
namespace: velero
spec:
provider: vault
parameters:
vaultAddress: "https://vault.vault.svc:8200"
roleName: "velero"
objects: |
- objectName: cloud
secretPath: "kv/data/velero/s3"
secretKey: "cloud"
secretObjects:
- secretName: velero-s3-secret
type: Opaque
data:
- key: cloud
objectName: cloud
Pi-hole DNS Forwarder for Velero Namespace#
Ensures Velero pods resolve external S3 hostnames via my LAN Pi-hole DNS server.
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: coredns
namespace: kube-system
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: coredns
data:
Corefile: |
.:53 {
errors
health
ready
kubernetes cluster.local in-addr.arpa ip6.arpa {
pods insecure
fallthrough in-addr.arpa ip6.arpa
}
forward . 192.168.10.104
cache 30
loop
reload
loadbalance
}
3. Velero UI#
A lightweight dashboard for browsing backup jobs, restore points, and logs — deployed as a separate Argo CD Application.
Argo CD Application#
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Application
metadata:
name: velero-ui
namespace: argocd
finalizers:
- resources-finalizer.argocd.argoproj.io
spec:
project: homelab
destination:
server: https://kubernetes.default.svc
namespace: velero
sources:
- repoURL: git@github.com:whitehatcats/k3s-homelab-gitops.git
targetRevision: main
ref: values
- repoURL: https://otwld.github.io/helm-charts
chart: velero-ui
targetRevision: 0.14.0
helm:
valueFiles:
- $values/infra/velero-ui/values.yaml
- repoURL: git@github.com:whitehatcats/k3s-homelab-gitops.git
targetRevision: main
path: infra/velero-ui
syncPolicy:
automated:
prune: true
selfHeal: true
syncOptions:
- CreateNamespace=true
- PruneLast=true
- Validate=false
- DeletePropagationPolicy=foreground
Secret Management via Vault CSI#
UI Authentication Password#
This secret provides the admin password for the Velero Web UI login.
apiVersion: secrets-store.csi.x-k8s.io/v1
kind: SecretProviderClass
metadata:
name: velero-ui-auth
namespace: velero
spec:
provider: vault
parameters:
vaultAddress: "https://vault.vault.svc:8200"
vaultMountPath: "kubernetes"
roleName: "velero"
vaultTLSCaCert: "/vault/userconfig/ca/ca.crt"
objects: |
- objectName: "password"
secretPath: "kv/data/velero/ui-auth"
secretKey: "password"
secretObjects:
- secretName: velero-ui-auth
type: Opaque
data:
- objectName: "password"
key: password
Encryption / JWT Passphrase#
This secret provides the passphrase used internally by Velero UI for JWT signing and encryption of backup data.
apiVersion: secrets-store.csi.x-k8s.io/v1
kind: SecretProviderClass
metadata:
name: velero-ui-secret
namespace: velero
spec:
provider: vault
parameters:
vaultAddress: "https://vault.vault.svc:8200"
vaultMountPath: "kubernetes"
roleName: "velero"
vaultTLSCaCert: "/vault/userconfig/ca/ca.crt"
objects: |
- objectName: "pass_phrase"
secretPath: "kv/data/velero/ui"
secretKey: "pass_phrase"
secretObjects:
- secretName: velero-ui-secret
type: Opaque
data:
- objectName: "pass_phrase"
key: pass_phrase
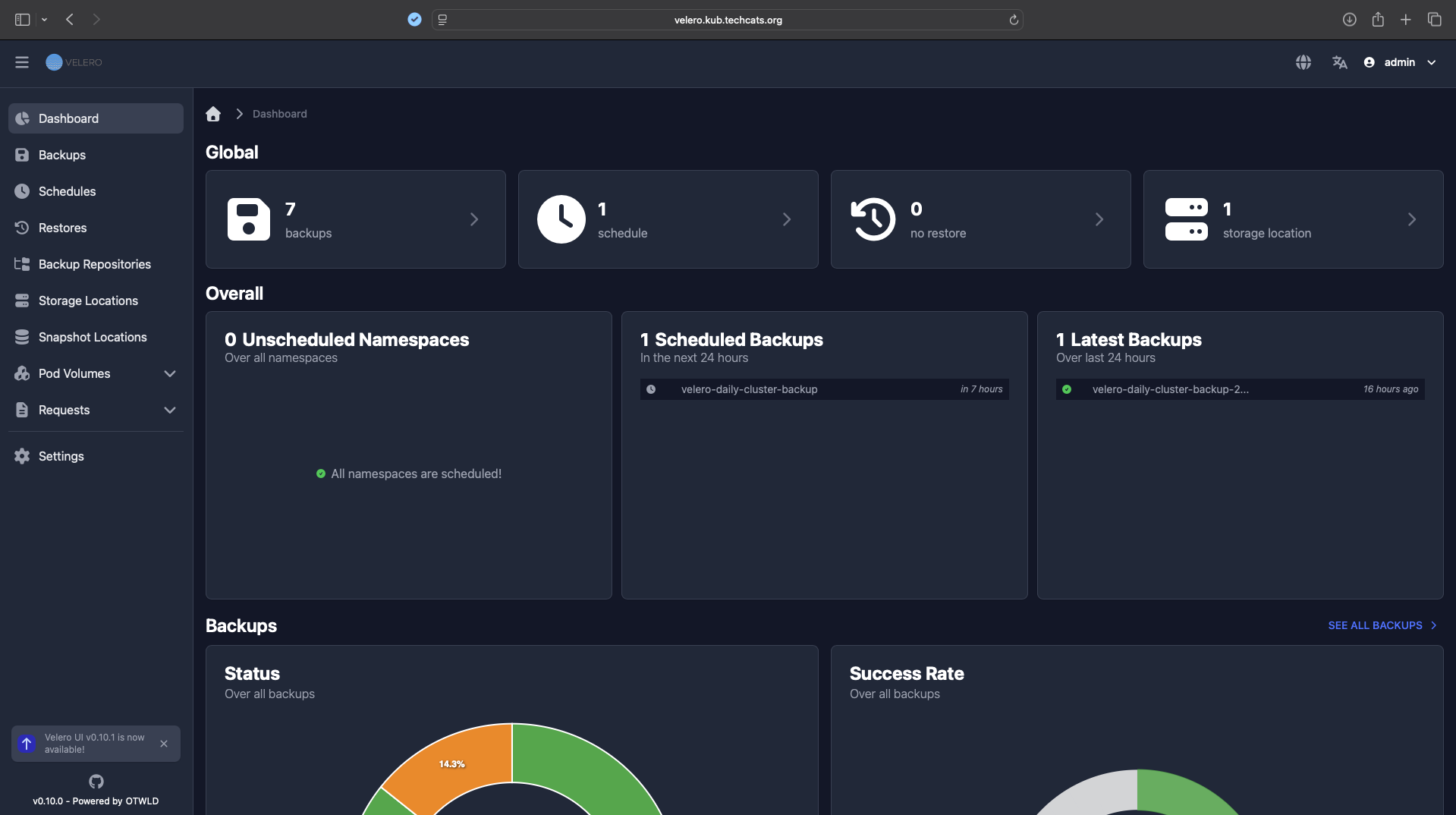
4. MinIO Object Storage#
MinIO provides an S3-compatible API endpoint for Velero backups.
It is deployed separately on a Docker host and accessed via HTTPS.
Docker Compose for MinIO#
services:
minio:
image: quay.io/minio/minio:latest
container_name: minio
restart: unless-stopped
command: server /data --console-address ":9001"
environment:
MINIO_ROOT_USER: ${MINIO_ROOT_USER}
MINIO_ROOT_PASSWORD: ${MINIO_ROOT_PASSWORD}
volumes:
- /home/daniel/share/minio-data:/data
- /home/daniel/docker/minio/config:/root/.minio
networks:
- proxy
labels:
- "traefik.enable=true"
- "traefik.http.routers.minio-api.rule=Host(`minio-api.techcats.org`)"
- "traefik.http.routers.minio-api.entrypoints=https"
- "traefik.http.routers.minio-api.tls.certresolver=cloudflare"
- "traefik.http.services.minio-api.loadbalancer.server.port=9000"
- "traefik.http.routers.minio-api.service=minio-api"
- "traefik.http.routers.minio-console.rule=Host(`minio.techcats.org`)"
- "traefik.http.routers.minio-console.entrypoints=https"
- "traefik.http.routers.minio-console.tls.certresolver=cloudflare"
- "traefik.http.services.minio-console.loadbalancer.server.port=9001"
- "traefik.http.routers.minio-console.service=minio-console"
networks:
proxy:
external: true
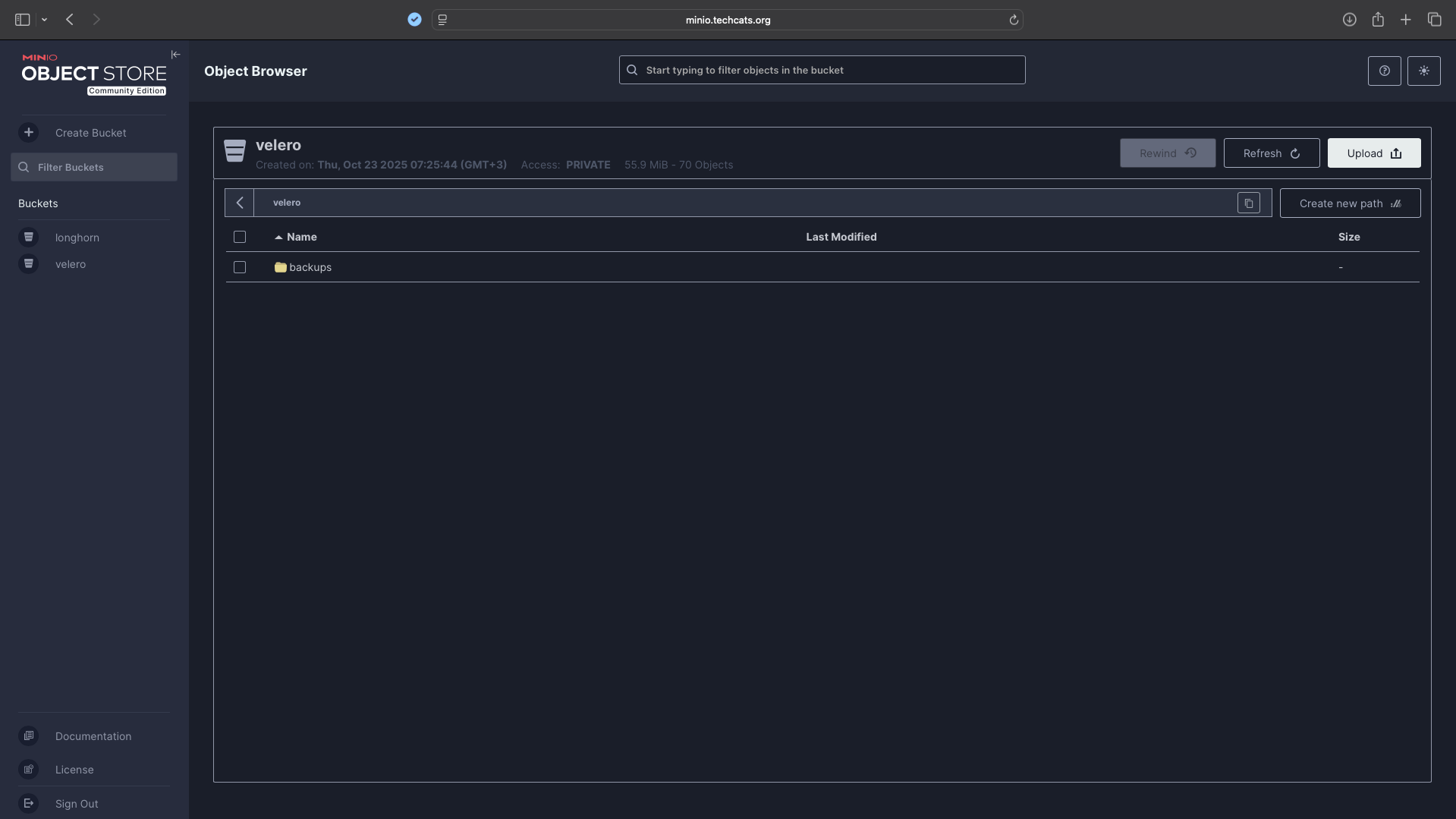
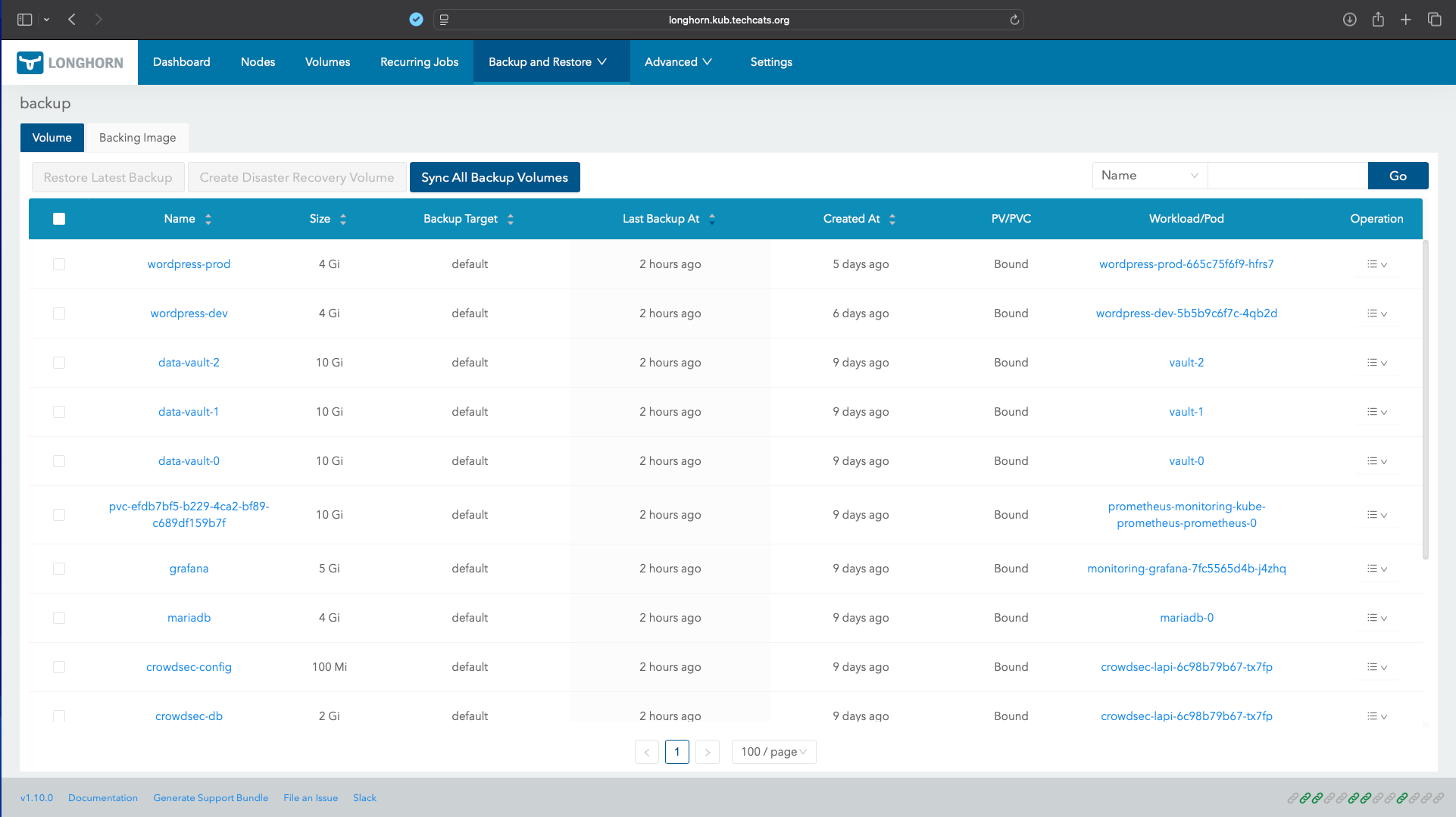
5. Backup Scheduling & Monitoring#
Velero runs a daily scheduled backup: Schedule: 0 3 * * * Retention: 7 days (ttl: 168h)
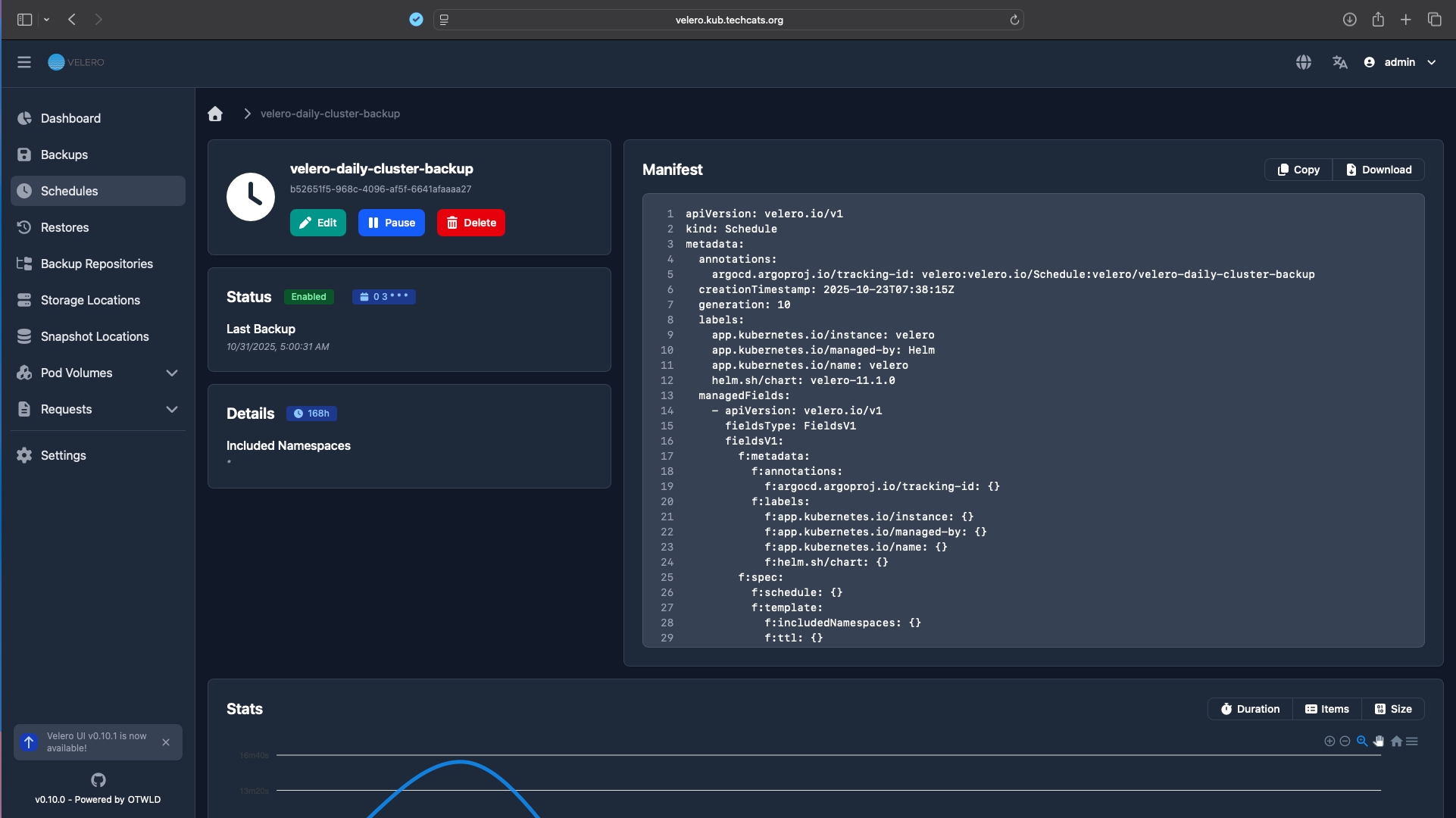
Includes all namespaces and PVCs managed by Longhorn Backups are visible both via Longhorn and Velero UI.
Key Takeaways#
- Vault CSI secures credentials and eliminates plaintext secrets.
- MinIO provides local, cloud-compatible S3 storage.
- Velero ensures consistent, automated backups of Kubernetes resources and PVCs.
- Argo CD maintains full declarative control, ensuring repeatable recovery.
- Longhorn CSI enables reliable snapshot creation and restore operations.
Conclusion#
This GitOps-based backup system provides a reproducible and secure approach to data protection in Kubernetes environments.
By combining Velero, Vault CSI, Longhorn, and MinIO, it ensures end-to-end automation—from snapshot creation to encrypted off-cluster storage.
