Overview#
This post documents the deployment of a TLS-enabled, highly available HashiCorp Vault cluster on Kubernetes.
The setup is managed entirely through GitOps using Argo CD, providing declarative configuration, automated reconciliation, and version-controlled infrastructure.
Vault runs in HA mode with Raft integrated storage, and all communication is encrypted with certificates issued by cert-manager.
It serves as the core of the homelab’s secrets management stack — integrated with Traefik for secure ingress and with the CSI driver for secret injection into workloads.
The architecture below illustrates the complete Vault deployment, from certificate management and ingress to secret delivery via the CSI driver.
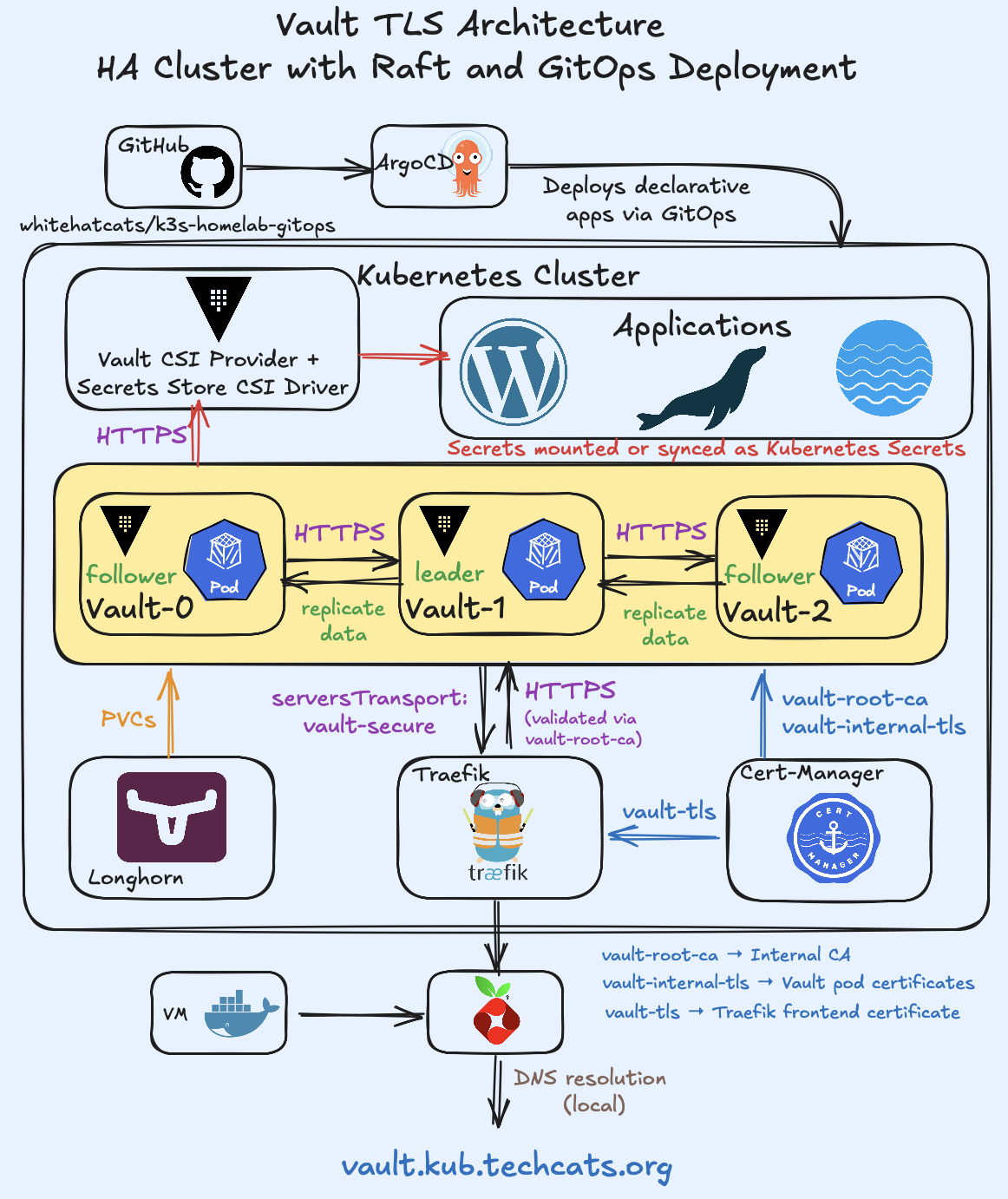
Vault#
Vault acts as the central secrets authority within the cluster.
It stores and manages sensitive data such as credentials, tokens, and certificates, providing access to workloads through Kubernetes authentication and the Vault CSI Provider.
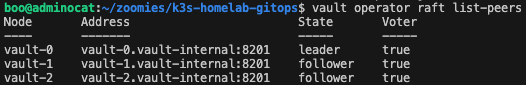
The deployment uses Raft integrated storage for high availability and persistent Longhorn volumes for durability.
All configuration, TLS setup, and lifecycle management are handled declaratively via Argo CD.
Helm Values#
Vault is deployed using the official HashiCorp Helm chart, configured for high availability with Raft integrated storage.
Persistent data is stored on Longhorn, and all traffic is encrypted using certificates issued by cert-manager.
# Excerpt from values.yaml
# ============================================================
# Vault | TLS Enabled, HA with Raft Storage
# ============================================================
global:
enabled: true
tlsDisable: false
server:
logLevel: info
logFormat: json
# ----------------------------------------------------------
# TLS Certificates (mounted from cert-manager Secret)
# ----------------------------------------------------------
extraEnvironmentVars:
VAULT_CACERT: /vault/userconfig/tls/vault-internal-tls/ca.crt
VAULT_TLSCERT: /vault/userconfig/tls/vault-internal-tls/tls.crt
VAULT_TLSKEY: /vault/userconfig/tls/vault-internal-tls/tls.key
extraVolumes:
- type: secret
name: vault-internal-tls
path: /vault/userconfig/tls
# ----------------------------------------------------------
# Persistent Storage
# ----------------------------------------------------------
dataStorage:
enabled: true
size: 10Gi
storageClass: longhorn-retain
# ----------------------------------------------------------
# High Availability - Raft
# ----------------------------------------------------------
ha:
enabled: true
replicas: 3
raft:
enabled: true
setNodeId: true
config: |
ui = true
cluster_name = "vault-cluster"
api_addr = "https://$(HOSTNAME).vault-internal.vault.svc.cluster.local:8200"
cluster_addr = "https://$(HOSTNAME).vault-internal.vault.svc.cluster.local:8201"
listener "tcp" {
address = "[::]:8200"
cluster_address = "[::]:8201"
tls_cert_file = "/vault/userconfig/tls/vault-internal-tls/tls.crt"
tls_key_file = "/vault/userconfig/tls/vault-internal-tls/tls.key"
tls_client_ca_file = "/vault/userconfig/tls/vault-internal-tls/ca.crt"
}
storage "raft" {
path = "/vault/data"
retry_join {
leader_api_addr = "https://vault-0.vault-internal.vault.svc.cluster.local:8200"
leader_ca_cert_file = "/vault/userconfig/tls/vault-internal-tls/ca.crt"
leader_client_cert_file = "/vault/userconfig/tls/vault-internal-tls/tls.crt"
leader_client_key_file = "/vault/userconfig/tls/vault-internal-tls/tls.key"
}
retry_join {
leader_api_addr = "https://vault-1.vault-internal.vault.svc.cluster.local:8200"
leader_ca_cert_file = "/vault/userconfig/tls/vault-internal-tls/ca.crt"
leader_client_cert_file = "/vault/userconfig/tls/vault-internal-tls/tls.crt"
leader_client_key_file = "/vault/userconfig/tls/vault-internal-tls/tls.key"
}
retry_join {
leader_api_addr = "https://vault-2.vault-internal.vault.svc.cluster.local:8200"
leader_ca_cert_file = "/vault/userconfig/tls/vault-internal-tls/ca.crt"
leader_client_cert_file = "/vault/userconfig/tls/vault-internal-tls/tls.crt"
leader_client_key_file = "/vault/userconfig/tls/vault-internal-tls/tls.key"
}
}
disable_mlock = true
service_registration "kubernetes" {}
telemetry {
prometheus_retention_time = "30s"
disable_hostname = true
}
# ============================================================
# Prometheus Telemetry Integration
# ============================================================
serverTelemetry:
serviceMonitor:
enabled: true
interval: 30s
scrapeTimeout: 10s
tlsConfig:
insecureSkipVerify: false
serverName: vault.vault.svc
ca:
secret:
name: vault-metrics-client
key: ca.crt
authorization:
credentials:
name: prometheus-token
key: token
selectors:
release: prometheus
TLS#
TLS encrypts all Vault traffic — both internal (between pods) and external (through Traefik).
Certificates are automated by cert-manager, following a layered trust chain where each level has a specific role in securing communication and establishing mutual authentication.
Certificate Hierarchy#
| Certificate | Purpose | Signed By | Used For |
|---|---|---|---|
| vault-root-ca | Root of trust (Cluster CA) | Self-signed | Signs all Vault certificates |
| vault-ca-issuer | cert-manager issuer for Vault | vault-root-ca | Issues internal Vault certs |
| vault-internal-tls | Internal TLS for Raft and API | vault-ca-issuer | Secures pod-to-pod and API traffic |
| vault-tls | Public certificate for Vault UI | Let’s Encrypt | HTTPS access via Traefik |
This hierarchy ensures both internal Vault communication and external access through Traefik remain encrypted and verifiable through the appropriate certificate authority.
Root and Issuer Configuration#
The following resources define the internal CA chain for Vault.
A self-signed ClusterIssuer establishes the root of trust, a Certificate creates the long-lived root CA, and an Issuer in the Vault namespace delegates signing authority for internal certificates.
# Excerpt from internal-ca/ci-vault-selfsigned-root.yaml
# ============================================================
# ClusterIssuer | Vault Self-Signed Root
# ============================================================
apiVersion: cert-manager.io/v1
kind: ClusterIssuer
metadata:
name: vault-selfsigned-root
spec:
selfSigned: {}
---
# Excerpt from internal-ca/cert-vault-root-ca.yaml
# ============================================================
# Certificate | Vault Root CA (Self-Signed)
# ============================================================
apiVersion: cert-manager.io/v1
kind: Certificate
metadata:
name: vault-root-ca
namespace: vault
spec:
isCA: true
commonName: vault-root-ca
secretName: vault-root-ca
duration: 87600h # 10 years
renewBefore: 720h
privateKey:
algorithm: RSA
size: 2048
usages:
- cert sign
- crl sign
issuerRef:
name: vault-selfsigned-root
kind: ClusterIssuer
---
# Excerpt from internal-ca/issuer-vault-ca.yaml
# ============================================================
# Issuer | Vault CA (Signs Vault TLS Certificates)
# ============================================================
apiVersion: cert-manager.io/v1
kind: Issuer
metadata:
name: vault-ca-issuer
namespace: vault
spec:
ca:
secretName: vault-root-ca
Internal TLS Certificate#
Vault pods mount the vault-internal-tls certificate to secure Raft replication and HTTPS API traffic.
The certificate includes Subject Alternative Names (SANs) for all Vault pod DNS records, ensuring that every instance can authenticate its peers through mutual TLS.
# Excerpt from internal-ca/cert-vault-internal.yaml
# ============================================================
# Certificate | Vault Internal TLS
# ============================================================
apiVersion: cert-manager.io/v1
kind: Certificate
metadata:
name: vault-internal-tls
namespace: vault
spec:
secretName: vault-internal-tls
commonName: vault.vault.svc
dnsNames:
- vault.vault.svc
- vault.vault.svc.cluster.local
- '*.vault.vault.svc'
- '*.vault.vault.svc.cluster.local'
- vault-0.vault-internal.vault.svc
- vault-1.vault-internal.vault.svc
- vault-2.vault-internal.vault.svc
ipAddresses:
- 127.0.0.1
duration: 8760h
renewBefore: 240h
privateKey:
algorithm: RSA
size: 2048
usages:
- digital signature
- key encipherment
- server auth
issuerRef:
name: vault-ca-issuer
kind: Issuer
UI TLS Certificate#
The Vault UI exposed through Traefik uses a certificate obtained from Let’s Encrypt, but the endpoint itself is not publicly accessible.
All traffic to vault.kub.techcats.org is resolved locally through Pi-hole, ensuring that access remains private within the homelab network.
The certificate is still issued and automatically renewed by cert-manager using a DNS-01 challenge, allowing secure HTTPS communication and full automation even for internal domains.
# Excerpt from resources/cert-vault.yaml
# ============================================================
# Certificate | Vault UI TLS
# ============================================================
apiVersion: cert-manager.io/v1
kind: Certificate
metadata:
name: vault-tls
namespace: vault
spec:
secretName: vault-tls-secret
issuerRef:
name: letsencrypt-vault-issuer
kind: ClusterIssuer
commonName: vault.kub.techcats.org
dnsNames:
- vault.kub.techcats.org
duration: 2160h # 90 days
renewBefore: 360h # Renew 15 days before expiry
Together, these certificates create a secure setup with an internal CA for Vault’s internal traffic and a Let’s Encrypt certificate for the web interface.
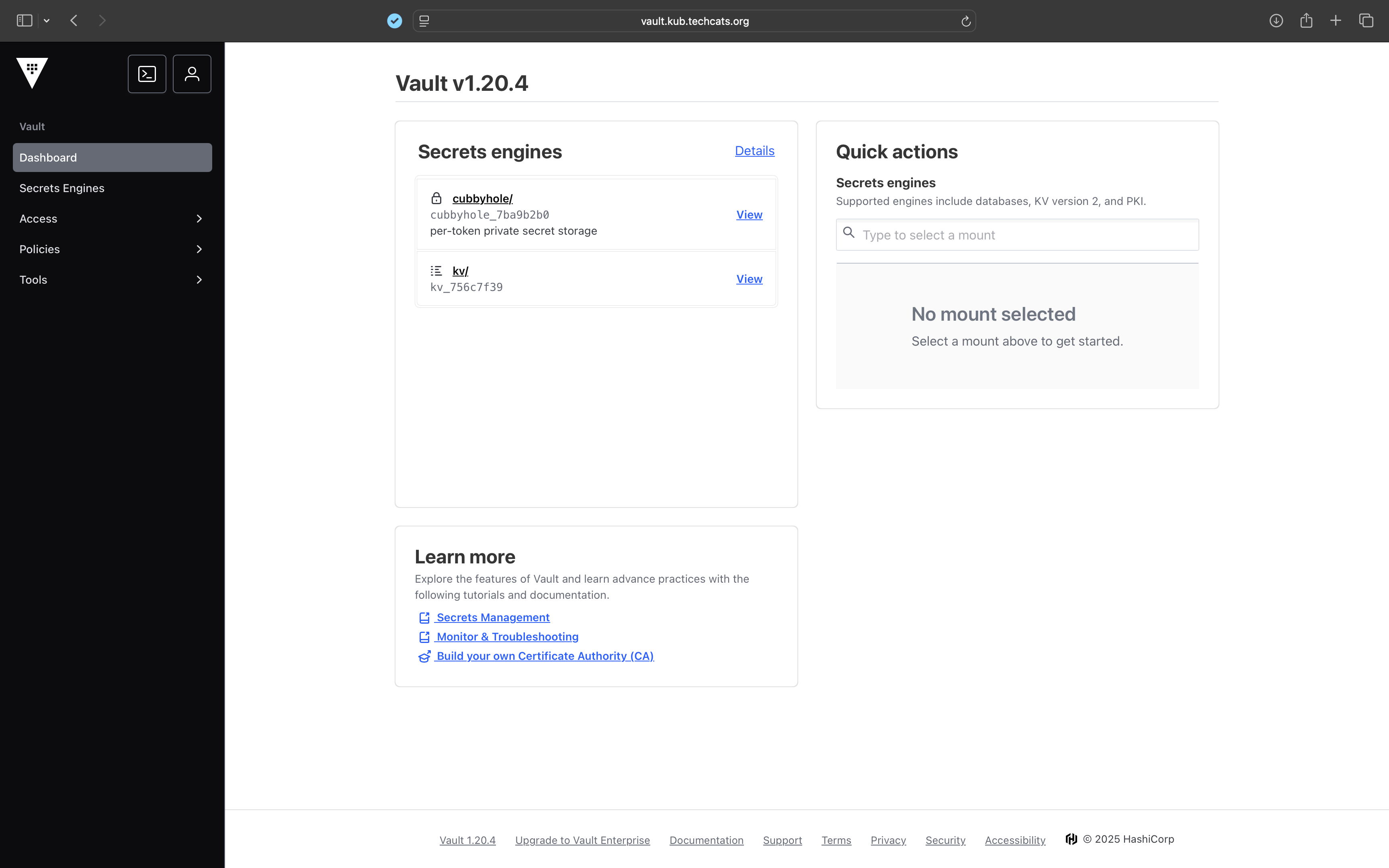
vault.kub.techcats.org over HTTPS. The interface confirms that the cluster is initialized and TLS-enabled, with active secrets engines mounted.Traefik Connection#
Vault runs with internal TLS enabled, which means Traefik must establish a trusted HTTPS connection when proxying requests to the Vault backend service.
The ServersTransport resource below defines how Traefik verifies Vault’s certificate using the internal CA (vault-root-ca), ensuring end-to-end encryption between Traefik and Vault.
# Excerpt from resources/st-vault.yaml
# ============================================================
# ServersTransport | Vault Secure Connection
# ============================================================
apiVersion: traefik.io/v1alpha1
kind: ServersTransport
metadata:
name: vault-secure
namespace: vault
spec:
rootCAsSecrets:
- vault-root-ca
serverName: vault.vault.svc
insecureSkipVerify: false
CSI Provider#
The Vault CSI provider extends Vault integration into Kubernetes, allowing workloads to mount secrets directly from Vault or sync them as native Kubernetes Secrets.
It operates alongside the main Vault instance but is deployed as a separate Argo CD Application, maintaining independent lifecycle management within the GitOps workflow.
The configuration below enables the CSI driver component inside the Vault Helm chart and configures it to communicate securely with the existing Vault service using the internal CA certificate.
# Excerpt from vault-csi-provider/values.yaml
# ============================================================
# Vault CSI Provider Configuration
# ============================================================
server:
enabled: false
injector:
enabled: false
csi:
enabled: true
agent:
enabled: true
extraArgs:
- "-vault-addr=https://vault.vault.svc:8200"
- "-vault-tls-ca-cert=/vault/userconfig/ca/ca.crt"
- "-log-level=debug"
volumes:
- name: vault-root-ca
secret:
secretName: vault-root-ca
items:
- key: ca.crt
path: ca.crt
volumeMounts:
- name: vault-root-ca
mountPath: /vault/userconfig/ca
readOnly: true
CSI Driver#
The Secrets Store CSI Driver (by kubernetes-sigs) mounts secrets from external managers such as Vault into Kubernetes pods.
It runs as a separate Argo CD application and works with the Vault CSI provider to deliver secrets securely.
# Excerpt from csi-driver/values.yaml
# ============================================================
# Secrets Store CSI Driver Configuration
# ============================================================
syncSecret:
enabled: true
enableSecretRotation: false
linux:
enabled: true
Backup and Recovery#
Cluster-level backups are automated through Velero, ensuring data resilience for all namespaces and persistent volumes.
Velero runs a daily scheduled backup with the following configuration:
- Schedule:
0 3 * * * - Retention: 7 days (
ttl: 168h)
The entire backup process and configuration are documented in detail here.
Key Takeaways#
- End-to-end TLS with internal CA and Let’s Encrypt automation
- HA Vault with Raft backend
- Dynamic secrets via CSI integration
- Fully declarative deployment through Argo CD
Repository & Implementation#
All manifests, overlays, and Helm configurations are version-controlled in Git and deployed via Argo CD.
Full implementation available at whitehatcats/k3s-homelab-gitops.
References#
- HashiCorp Vault Helm Chart — official Helm chart for deploying Vault on Kubernetes
- Vault Raft Storage Tutorial — guide to configuring Vault with integrated Raft storage
- Secrets Store CSI Driver Helm Chart — Kubernetes SIGs chart for managing external secret stores
- Traefik Services / Load-Balancing Documentation — reference for how Traefik defines and uses backend services
- Traefik ServersTransport CRD (Kubernetes) — official documentation for the
ServersTransportCRD in Traefik
